
06 8月 Aluminum Degassing Process
Aluminum Degassing Process
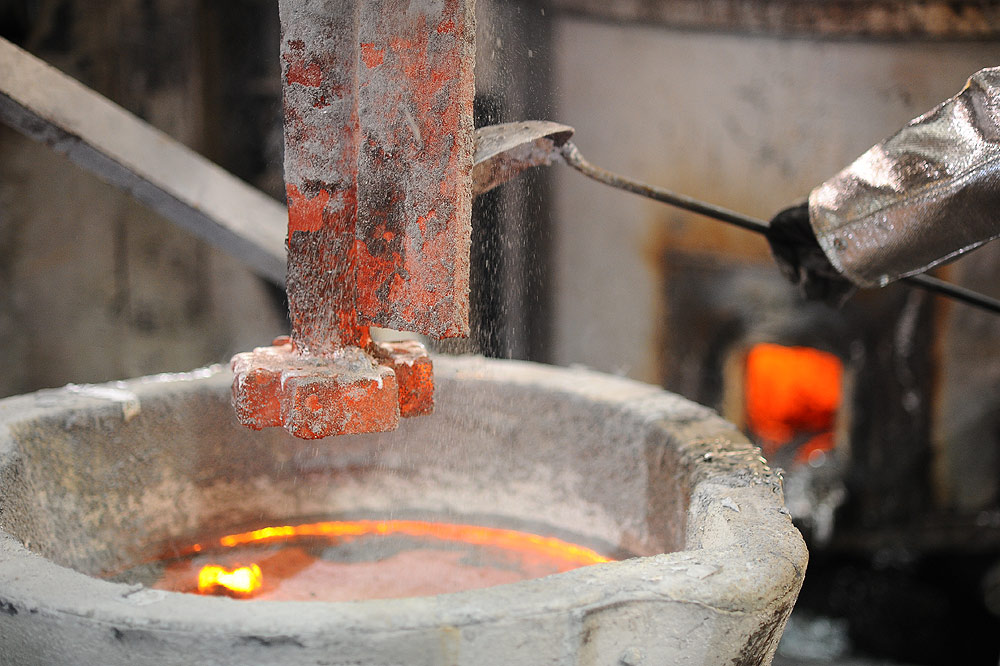
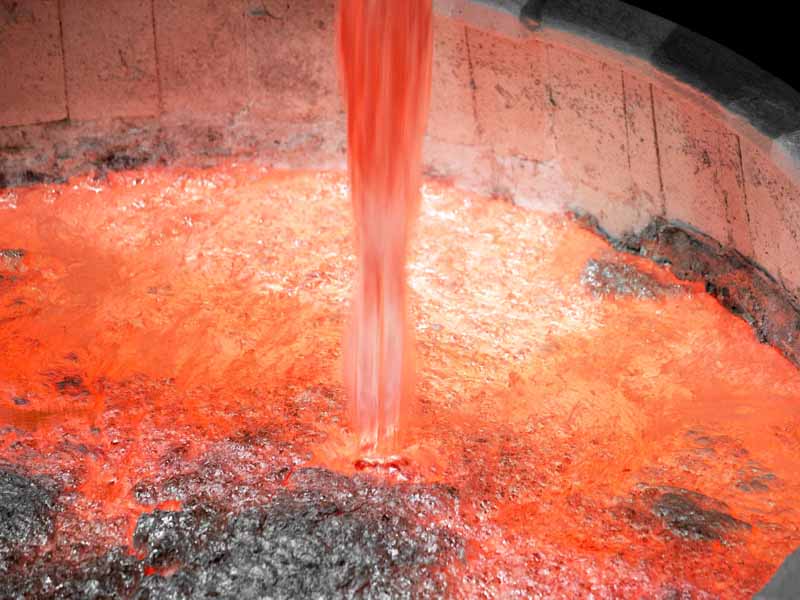
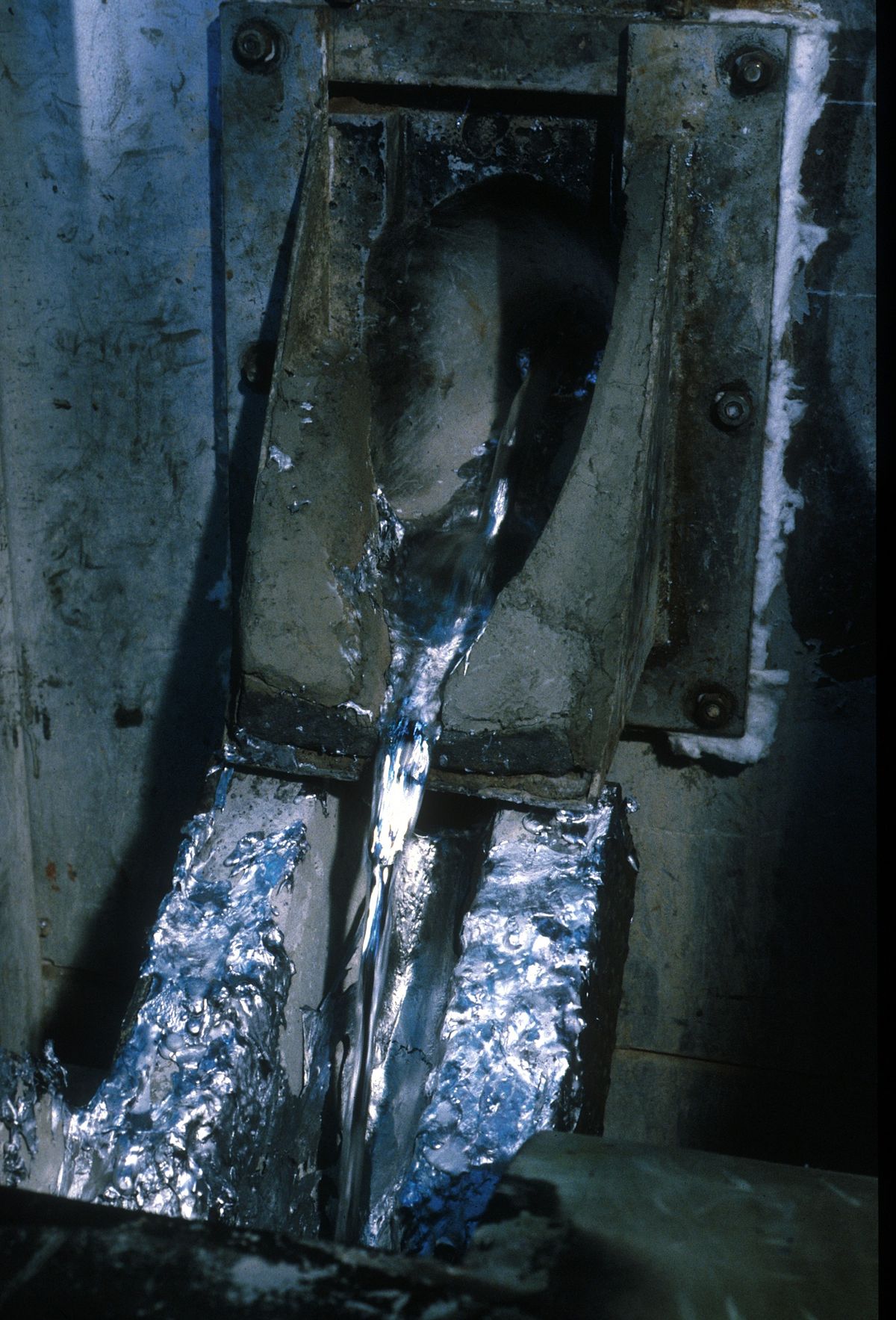
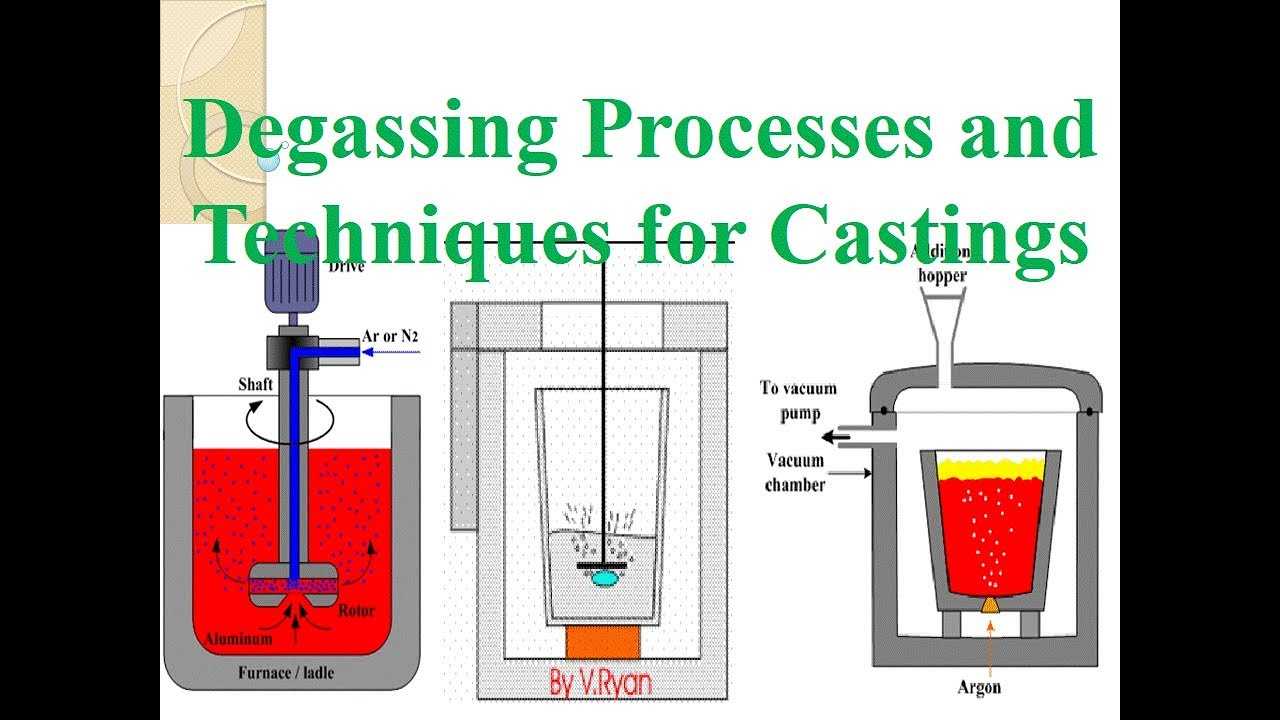
Aluminum Degassing Process Use a graphite lance to bubble nitrogen through the molten aluminum before I pour it.
It will guarantee you don’t have any gas pin holes in your castings.
I usually just do it when I’m casting a piece that has to be highly polished.
Other then that I just use a little Coveral flux, commercial stuff.
If you watch your temperature, use clean aluminum and don’t take too long to get the melts ready to pour you can get by with using very little flux and you won’t have gassy melts either.
Aluminum Degassing Process
Those who purge with nitrogen will notice sparks igniting as the hydrogen marries with it [i.e., the nitrogen] and comes out of solution [the hydrogen] and back to a gas [in the bubbles off the metal].

Nitrogen is extraordinarily unreactive and I don’t see it doing anything with mere aluminum and hydrogen at this temperature and pressure.
It could combine with magnesium content, but aluminum alloys are generally unreactive, even with magnesium. As others have noticed, bulk magnesium mistakenly added can bring the pot to burning, in oxygen, CO2 or nitrogen, especially when hot, where magnesium’s vapor pressure is high, much like zinc in molten bronze.
Commercial synthesis of ammonia (NH3, the direct result of combining hydrogen and nitrogen involves a catalyst (platinum, iron, etc.), similar temperatures and extreme pressures (~300 atm, or >4500 PSI) in order to force the nitrogen and hydrogen together.
Even so, yield is low and the outgoing gas has to be processed (ammonia is condensed and the hydrogen and nitrogen cycle back for another go).
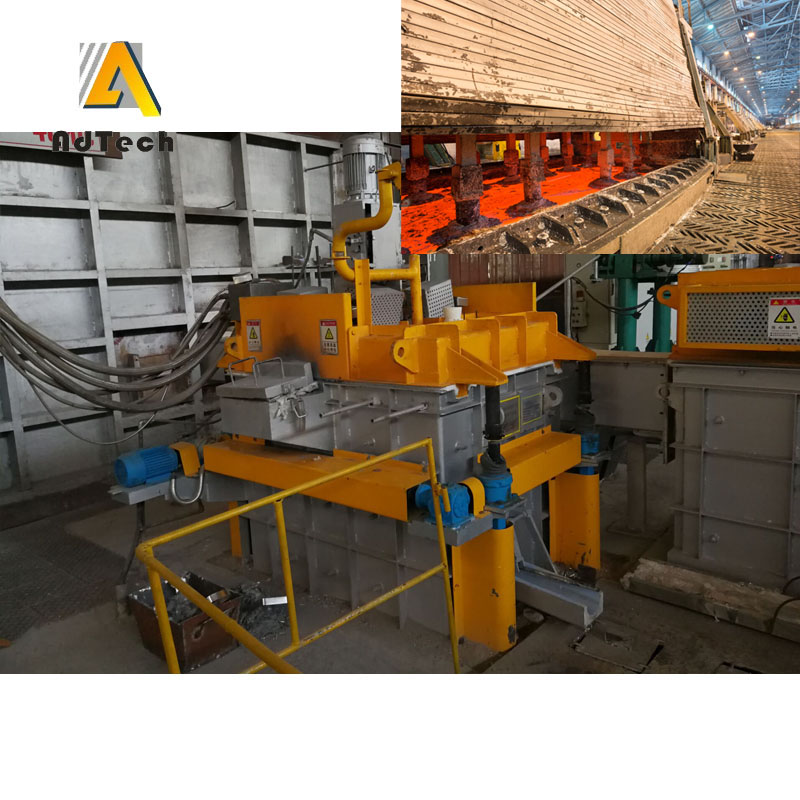
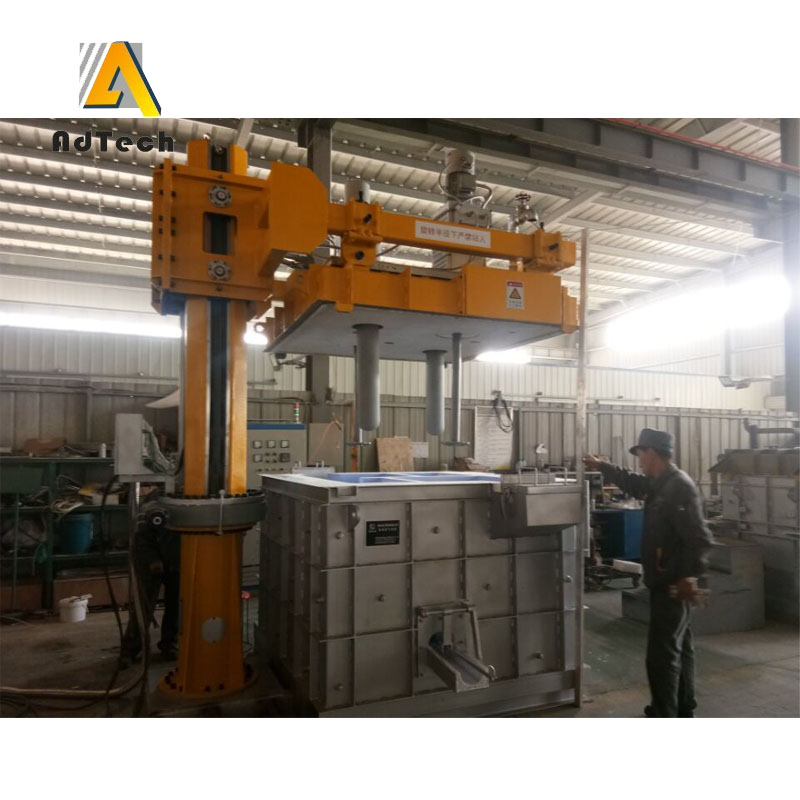
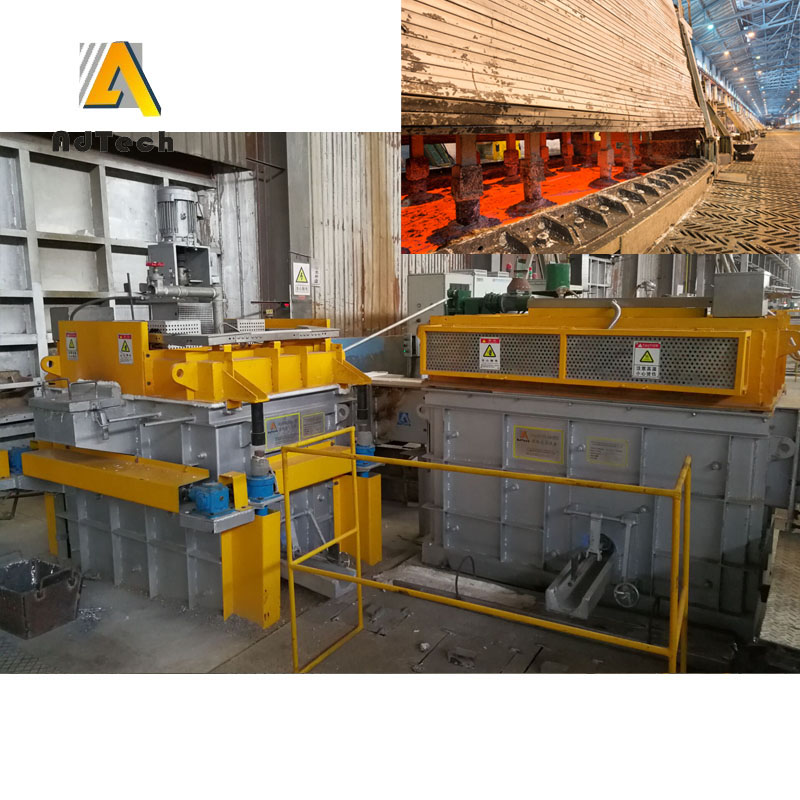
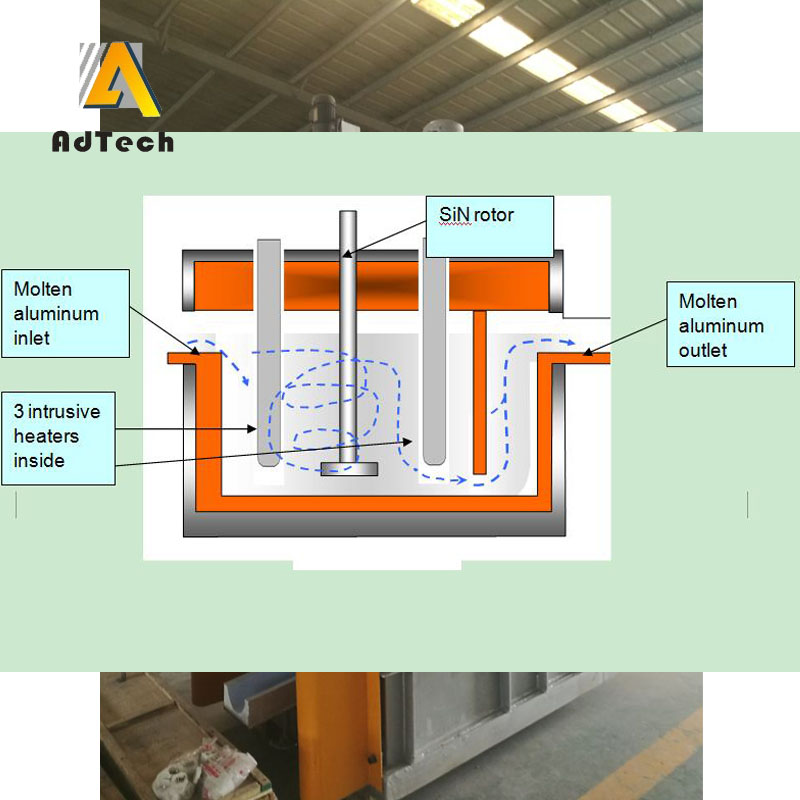
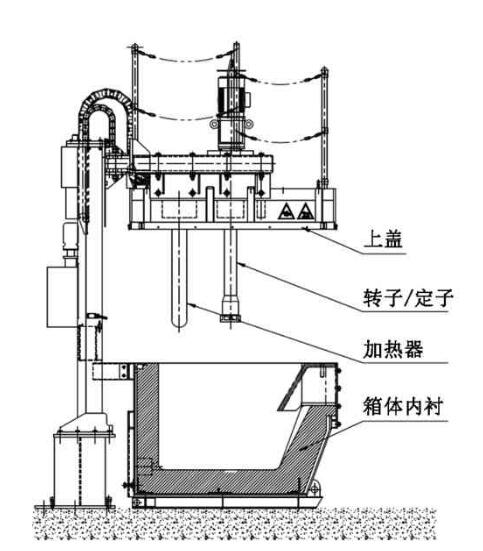
Online Degassing Unit
Online Degassing Unit is to remove hydrogen, non-metallic inclusions and unwanted trace elements. The refining is normally done after alloy addition. In some cases the melt is also pre-treated before alloying. Gas injection is the most commonly used refining method.
A gas in Aluminum Degassing Process is injected through porous bottom, nozzles in the bottom or walls, through lances (with or without porous ends) or through rotating impellers. Gases used are nitrogen, argon and chlorine as well as gas mixtures of said gases.
The purpose of bubbling in the Aluminum Degassing Process, a gas (inert to Al, for obvious reasons) is to draw hydrogen out. Dissolved gasses have a certain vapor pressure at the liquid surface, so continually adding dry (i.e., little of what you’re trying to remove) gas will drive the equilibrium to “dry” in the liquid.












Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.