
25 2月 Ceramic Foam Filter Manufacturer Process
Ceramic Foam Filter Manufacturer Process
Ceramic Foam Filter Manufacturer Process-Ceramic Foam Filter Transmittance
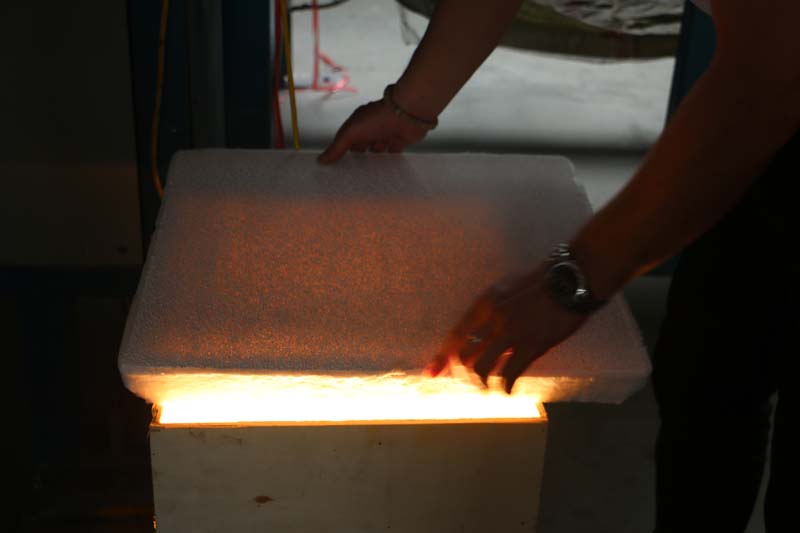
The foam ceramic filter plate to be inspected is placed on a light box with a built-in 200W incandescent bulb, and a square transparent plastic plate with a uniform 5.0×5.0 mm square is used to measure the light transmissive area of the large surface of the filter plate, thereby calculating the test. The light transmittance of the filter plate is used to determine the light transmittance of the filter plate.
In this standard, the light transmittance (through hole ratio) of the filter plate is specified to be 95% or more. Porosity is the percentage of the total volume of the cavities in the filter plate product to the total volume of the filter plate product. The porosity determines the filtration capacity of the foam ceramic filter plate per unit volume. The larger the porosity, the larger the filtration flow rate of the filter plate and the stronger the filtration capacity, and vice versa.

Ceramic Foam Filter Manufacturer Process-Determining Porosity
There are currently two main methods for determining porosity.
One is to calculate the volume of the hole in the filter plate according to Archimedes’ law, that is, to inject water into the glass beaker with the overflow pipe until the water flows out from the overflow pipe, and the water will be tested when the water is no longer flowing out. All the samples are gently placed in the water, then the water flows out of the overflow tube, and the volume of water in this part is measured. The volume of the overflow water is subtracted from the physical volume of the filter plate, which is the total volume of the holes in the filter plate. volume.
Another method is to separately determine the true density and bulk density of the sample to be tested, and then calculate the porosity of the sample according to the following formula.
These two methods have their own advantages and disadvantages. The method of operation is simple and convenient, and the detection speed is fast, but its fatal weakness is due to the water absorption characteristics of the filter plate material itself, so that the volume of water discharged is smaller than the actual one. This causes the measured data to be too small.
Although the test process of the second method is more complicated, the influence of the water absorption of the filter plate material is excluded during the test, and the obtained data is relatively accurate.
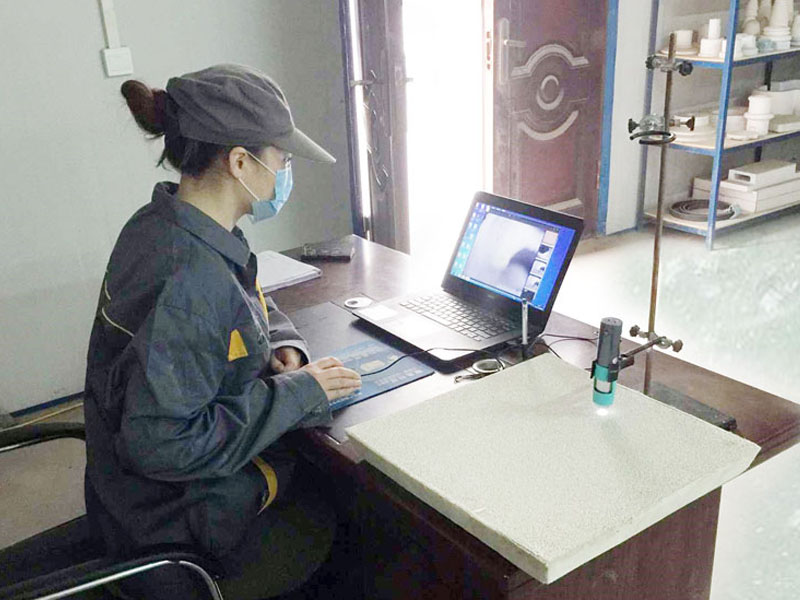

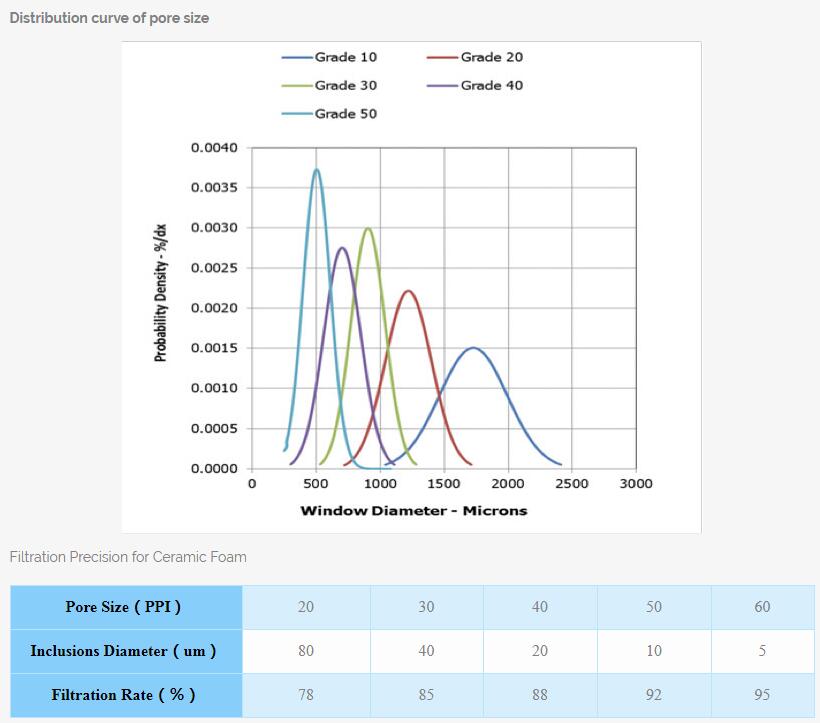
Ceramic Foam Filter Manufacturer Process-The Index of Porosity
The index of porosity is determined to be greater than 84% in this standard. Pore uniformity is used to describe the difference between the number of actual holes per 25.4 mm length in the filter plate product and the number of theoretically required holes.
The smaller the gap, the better the product quality, and the gap is too large, which will result in the ability of the filter plate product to reduce the impurity retention or the slow filtration rate of the melt, which can not meet the individual requirements of the user’s production.
The size of the pore uniformity mainly depends on the foam used in the production of the filter plate. The uniformity of the pores of the foam is good, and the uniformity of the pores of the filter plate is good, so the selection of the foam is extremely important.
(Number of holes in any 25.4mm length) 10p 7~13 20p 17~23 30p 27~33 40p 37~43 50p 47~53 60p 57~63 This standard determines the pore uniformity as the data required in the above table. During the transportation and use, the filter plate must withstand the impact of a certain pressure from the outside, so the index of compressive strength is also introduced in the standard as one of the basis for measuring the quality of the filter plate. The higher the compressive strength, the more durable the product, the better the quality, and vice versa.
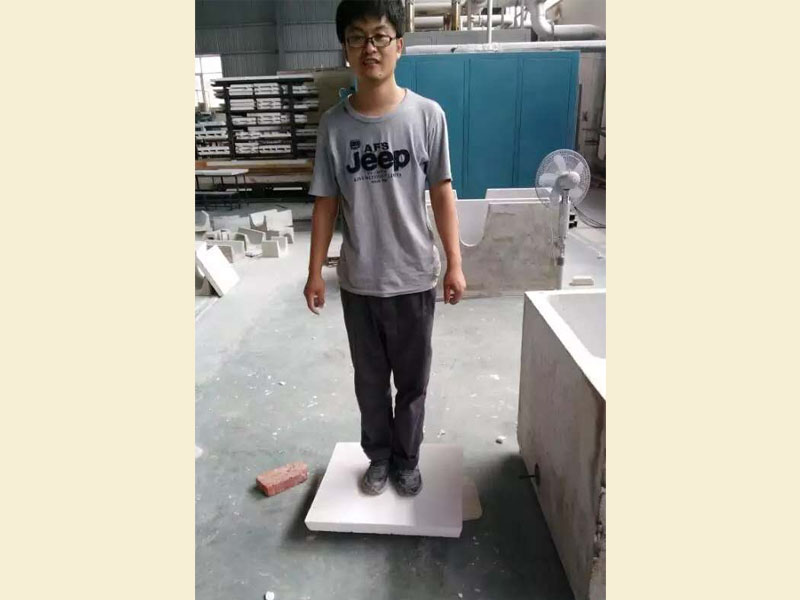
Ceramic Foam Filter Manufacturer Process-The Index of Compressive Strength
In this standard, the index of compressive strength is determined to be 0.5 MPa or more.
Thermal shock resistance refers to the resistance of ceramic filter plates to damage caused by rapid temperature changes.
During the use of the foam ceramic filter plate, we require the user to start the filtration before gradually heating the filter plate to the temperature of the filtered aluminum melt before use.
However, some users do not follow this rule very well when using it. After the filter plate is placed, the melt is filtered without preheating, which requires the filter plate to have a certain thermal shock resistance. The better the thermal shock resistance, the more durable the filter plate and the better the quality.














No Comments