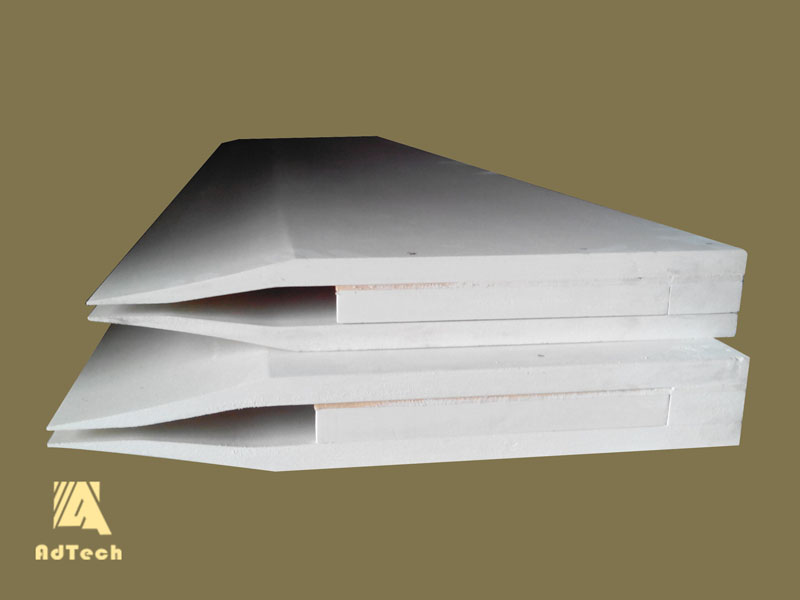

08 3月 Feeder Nozzle Cavity
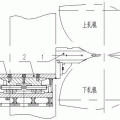
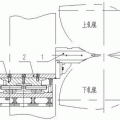
Feeder Nozzle Cavity casting nozzle support panel is a key component of the electromagnetic casting and rolling process, and its structural stability is directly related to the planar stability of the casting nozzle.
It is made of refractory fiber mat. The fiber mat contains approximately equal amounts of alumina and silica, and contains a solution containing colloidal silica.
The typical composition of the fiber is 51.2% alumina, 47.4% silica and 0.7% boron oxide and sodium oxide.
In order to make a suitable felt, these fibers are dispersed in an aqueous solution containing a colloidal silica dispersion.
By diluting the available components, the components contain about 30% colloidal silicon solids.
The average particle size of colloidal silica is about 17 microns, that is, about 48 silicon atoms per particle.
Colloidal silica is stabilized by sufficient alkali metal sodium hydroxide or lithium hydroxide in the solution, and the pH value is about 9.5 to 10.5.
This ingredient is diluted with water to form a solution containing approximately 22% colloidal silica solids by weight. Sufficient refractory fibers are dispersed in the solution to form a slurry of about 5% fibers.

If you need the Feeder Nozzle Cavity in the continuous casting and rolling process, please visit www.adtechamm.com or directly contact Sales@adtechamm.com
Generally, the spacing between the upstream portions of the two halves of the feed head is sufficient to maintain the required gap between the downstream edges of the casting head.
If required, one or more additional spacers can be provided in the middle between the upstream part and the downstream edge
. This gasket, if used, should be reasonably streamlined to avoid interference with the flow of metal through the feed end.
The space between the spacers provides a means for liquid metal to enter the gap between the two halves of the feed tip.
The cross-sectional area of the space at the upstream portion of the metal flow-through tip is preferably larger than the cross-sectional area of the gap between the downstream edges of the metal flow-through tip.
This ensures that the speed of the metal increases rather than decelerates as it passes through the tip.
The gap through which the molten metal flows between the upstream and the downstream is obviously tapered, which is also ideal for reducing the sudden change of the metal flow velocity at the top of the continuous casting machine.
This arrangement can minimize the discontinuity of metal flow and avoid the introduction of impurities in the thin plate formed by the continuous casting machine.
The substantially flat inner surface also allows the member to be thicker near the downstream edge and increase strength.














No Comments