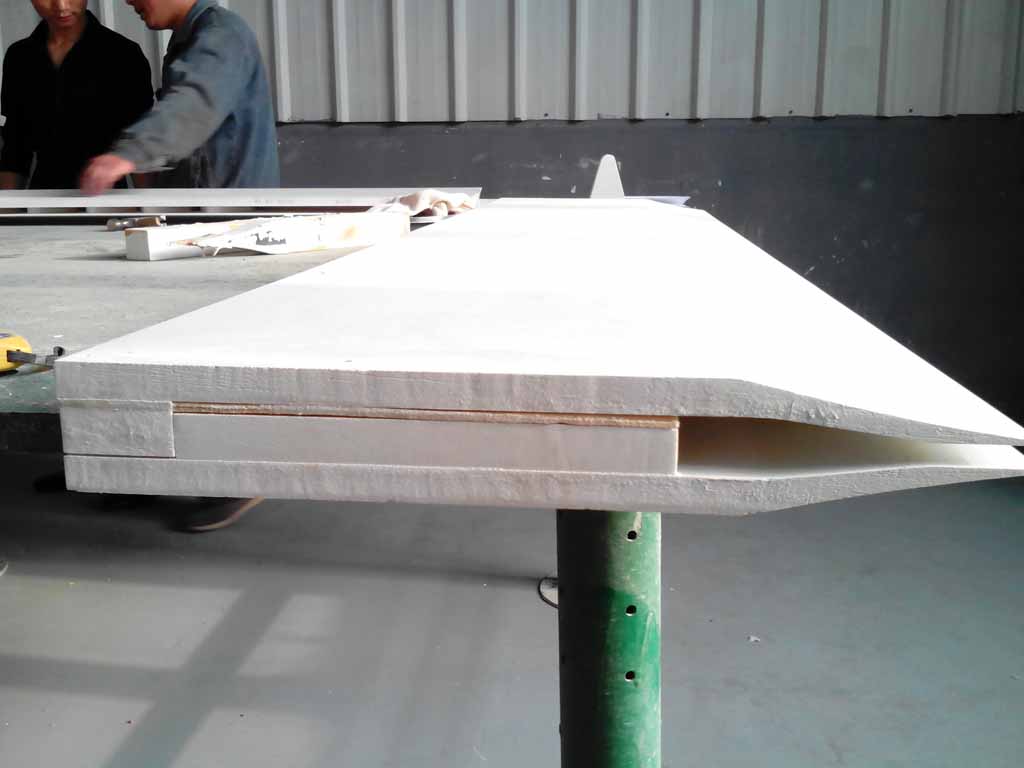

07 5月 Foundry Feeder Tip
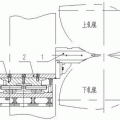
Foundry Feeder Tip is located in front of the rolls of rolling equipment in the aluminum alloy field and is used to guide molten aluminum alloy.
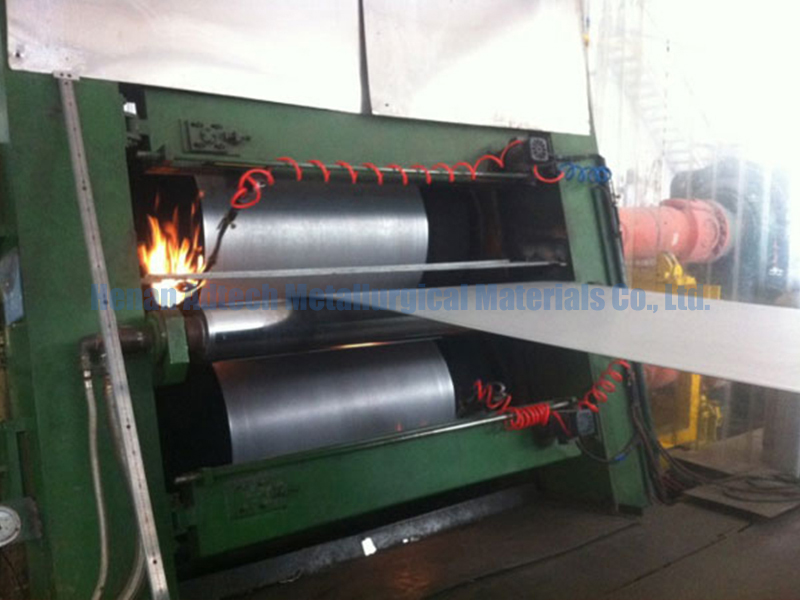
The molten aluminum enters the Feeder Tip from the rear inlet, and then exits from the front outlet, enters the rolls, where it is cooled by the rolls and rolled into a cast billet.
Usually the width of the cast-rolled billet is determined by the outlet width of the nozzle. In order to improve equipment utilization and reduce operating costs, the width of plates produced by ordinary casting and rolling equipment is relatively wide, generally reaching 1450mm-1600mm.
For cast-rolled slabs with a width of less than 800mm, if the traditional equipment structure and production method are used for production, the unit output will decrease.
The tip of the Foundry Feeder Tip is usually made of low-density ceramic material, which can withstand the wear and thermal shock of contact with liquid aluminum, such as a ceramic fiber board that is formed into the necessary shape.
Due to the low density of these materials, their thermal conductivity is very low (usually less than 0.18 W/mK), which can provide a certain degree of thermal insulation for the molten aluminum in the casting tip.
However, after a period of production, they may be corroded and worn by chemicals. This may lead to the formation of various impurities in the tip structure and eventually cause the casting movement to stop prematurely.

Feeder Tip usually produces the following erosion and wear
1.Castertip blocking
When a blockage occurs in the casttip cavity, the metal is restricted from flowing out of the entire width of the casttip opening, resulting in elongated pore defects on the surface of the cast-rolled strip.
The pores can be very small pores, which can be observed with the naked eye.
Sometimes, there are cavities inside the strip, and clear oxidation streaks can be seen on the surface of the strip.
The correction method is to increase the temperature of the metal. It is also possible to stop the rotation of the drum for a short time to allow the metal to solidify around the obstacle, and pull it out when restarting.
In some cases, blocked casttips require replacement of the nozzle plate.
Good refining measures are an effective way to prevent blockage of the cast slab.
2. Castertip scar
Metal solidification may occur inside the mouth or at the opening of the casting.
The metal solidifies in the oral cavity, which is manifested as a reduction in the width of the strip or the appearance of holes in the strip.
The cause of this defect may be metal leakage from the casting head or the low temperature of the metal in the nozzle plate.
The correction method is as follows:
·If the leakage is serious, replace the pouring nozzle plate
·Increase the temperature of the molten aluminum in the front box
·Improve casting speed
3. Fine ripples
This defect is manifested in some horizontally visible light and dark stripes on the surface of the cast-rolled steel strip. The symptoms of this defect are:
·The strip has horizontal dark stripes
·Rough edges
·The main motor current value drops
The reasons for this defect are:
·The metal level is too high. Due to the excessive metal pressure, the metal in the casttip will vibrate, causing fine waves on the surface of the board.
·Low casting speed
·Metal temperature is too high
Correction method: lower the liquid level of the front tank, lower the temperature of the aluminum liquid in the front tank, increase the casttip speed, and minimize defects.
Ideally, the heat distribution of the liquid metal leaving the casting tip is as uniform as possible along the length of the casting tip.
The width of the casting tip can be between 0.3 m and 2.5 m.
The molten aluminum leaving the casttip is usually at the hottest state in the center area and is insulated at the two outer ends of the tip.
The colder areas are usually located to the left and right of the center area, where the caster tips.
These temperature differences will affect the uniformity of the casting process and the quality of the cast steel strip.















No Comments